Here’s “Blame the Base-Cat”, my latest cartoon – there’s two versions.
US War Pigs
Here’s a “measure of justice” of the US, whose economy is primarily driven by dirty profits from weapons sales. May its predatory, planet-destroying empire which feasts on white supremacist oppression across the globe fall soon and hard.
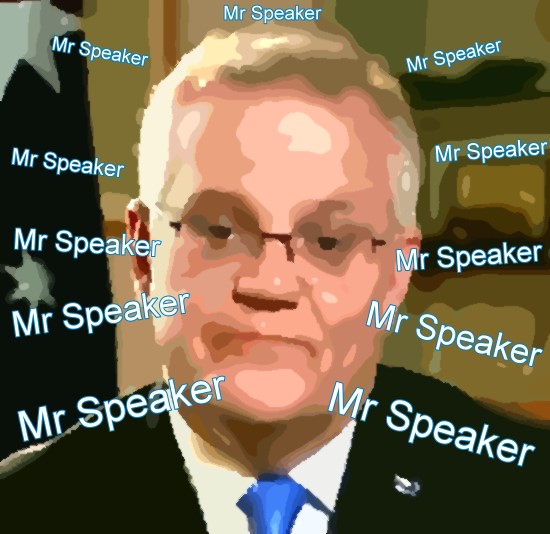
Mr Speaker Stand Up
Cando Bullshit
A lot of people from down south jibe and sneer at Queensland and us banana benders, especially those of us who don’t live in the city. You live 50 years in the past, they reckon. Well i’m here to tell you we in the Noosa hinterland are as erudite and edumacated as any of those Antarcticans. And if Queensland wasn’t so great, why have they been moving up here from down south in droves since the Covid hit? why do so many of them holiday in Noosa? why are they buying up all our houses?
So I decided to prove how in touch we are round here, by interviewing people in the local Cooran shop and asking them about our one and only prime monster, Scummo. Yeah, so Queensland gave Canberra the ghoulish Pauline Hanson, Malcolm Roberts, George Christenson, Matt Canavan, Potatohead and a couple of Mad Katters, but look what we got in return? and now he’s reckoning we can’t go to coffee shops in Briso? bollocks mate, we’ve barely noticed lockdowns. It’s him with his vaccine strollout who hasn’t noticed, the way he never notices how many times he says “Mr Speaker” in Question Time. But we notice.
Here’s a good one Laurie from round the corner told me.
A liar, a dogwhistling opportunist and an incompetent leader walk into a bar.
The bartender says “What can I get you, Mr Morrison?”
So you didn’t get it? wake the fuck up, Scummo relies on you mob being half asleep to pull the wool right over yer eyes.
Scummo doesn’t hold a hose to folks round these parts. As long time local Carol told me, the only hose he actually holds is his own and even then he doesn’t know what to do with it.
Then there’s Annie, who’s worked from home as an artist for years before covid. Here’s her sparkling wit.
This bloke went to a job interview and they asked about his work ethic.
He said, “I don’t give a fuck about my work colleagues getting death threats or raped or sexually harassed, just as long as someone takes lots of photos when I get a haircut instead of working.”
And they said …
Congratulations Prime Minister, when can you start?
Yeah, people round here are woke to Scummo’s foibles, we don’t put up with the prick. Terry reckoned he heard he could walk on water, but the real miracle is Scummo swims with the sharks down the Goldy and they line up on either side of him – it’s professional courtesy.
Scummo says it’s the Australian way, but what’s that? witch-burning? He’s taking us back to medieval times with this religious ‘freedom’ bill so nasty people can be racists and bigots again.
We’re not silly here, we all know religion’s just another blokey con job to keep us preggers in the kitchen and bringing the bloke his beer. Though it was a miracle Scummo got elected. That’s the last real truth I remember him telling us. My mate Jacky who works for the local rag, her journo mate down south asked him:
“Mr Morrison, what’s your favourite lie you’ve told the public?”
“I’ve never told a lie in public,” Scummo says.
“That’s my favourite too!” she replied.
Now he’s hawking hollow gibberish about climate change mitigation. We know he’s up to his eyeballs in coal, his precious. You can’t trust the bugger as far as you can throw him. The planet will fry, we’re all going to hell on earth, never mind the afterlife.
What’s the difference between Australia and hell?
Scott Morrison hasn’t managed to fuck up hell yet.
So what is a Morrison promise worth?
Net zero. Just ask the French.
Do you know what the mummy sardine said to the baby sardine when they saw the nuclear sub?
“Hey sonny, there goes a tin of scared Aussies.”
Now that’s critical technology, forty years late. When Scummo rants on about critical technology it reminds me of a joke at Tourism Australia when he was CEO, before he got the arse as he always does after his lies catch up with him. If his PA was off sick or on leave it was pointless expecting an answer to any emails. She wasn’t there to log him on to the system.
Scummo’s election pitch about government interferring in people’s lives is another joke. His same sex marriage bigotry, Indue card, Robodebt, alleged rape and FOI cover ups and religious discrimination laws all interfer in peoples’ lives. He talks from both sides of his mouth. Who else is sick of his coddling of neo-nazis? Just like his roll-out stroll-out … his call-out of the far right was a crawl-out. Ben at the shop told me this one.
What’s the difference between Neil Erikson and Scummo?
Neil is an honest self-proclaimed neo-Nazi.
Have I thrown you lot into enough of a spin yet?
Rightyo, folks, now I’m not going for a Scummo break – leaving in the middle of a crisis – I’m off to meet up with my mate from Melbourne who’s double vaxxed and tested clear so he can visit Queensland and not infect us the way Scummo wants us to be so he can claim a Labor state failed to do its job. Have a good one and remember to put the LNP crime family last on the ballot, the way they put our future last with their lies, dirty kick backs, net zero cred promises and pickled pork for their mates.
Jinjirrie
November 2021
(This is a standup exercise, to be performed in a broad Queensland accent.)
Addendum
Q. What’s the difference between #Omicron and #Scomicron?
A. One lays you out straight in bed, the other can’t lie straight in bed.
Incantations Against White Supremacism for Easter

Whitey’s Still on the Moon
Whitey gets a pass
because whitey is whitey
and white is right
whitey leads the fight
of the righteous struggle
of those oppressed
by benevolent whiteness
whitey’s the biggest victim
circling white wagons
benedictus benedictum
white saviour behaviour
honoured by whitey
for wealth and privilege
take up the white man’s burden
dissent is sacrilege
pre-ordained fame and fortune
whitey won the lucky dip
to captain white-sailed ships
first on the list
white supremacist
whitey’s got a ticket to ride
most active of activists
yachts to burn
marches to march
white gutless wonders watch
and silence is assent
quiet as white mice
no white divisiveness
of imperial solidarity
this exploitative opacity
colonise the colonised
the way it’s always been
whiteness is rightness
eternally blessed
the rough Beast’s in Jerusalem
Gil Scott Heron embraced BDS
and whitey’s on the moon still.
Jinjirrie, March 2018
Ball Tampering
They’ve lied once too often
to be trusted on their word
Craven politicians polish
yet another turd
The public’s asked to buy
a “Russian novichok”
While the greedy Toadball class
put us all in hock,
Cut those corporate taxes!
Give the rich another break!
It’ll trickle down to you scum
So our mates are on the take?
On military exports
the western world depends
Who cares if our warmongering
causes life on earth to end?
Jinjirrie, March 2018
The Sinking of the H.M.A.S. Grabbit
 Late night thoughts of Morriscum
Late night thoughts of Morriscum
set adrift in a leaky boat
with Australians online taking bets
how long he can stay afloat.
Abbott’s lashed firmly to the mast
Bishop’s locked in the hold
When the boat sinks we’ll all cheer
and divvy up the gold.
Brandis burnt international law
to please his zionist mates,
It won’t keep him warm 10 fathoms down
When he meets his watery fate.
Cormann’s whining on his mobile
calling up the crony banks
Too late for party kickbacks
the ocean gives us thanks.
For in all Australia’s history
there’s never been rogues as these
Corrupt and heartless brigands all
may they drown on the open seas.
Alas, the dream is but a dream
still the scurvy wretches spout
from their padded thrones in Parliament
We’ll have to vote them out.
Jinjirrie, July 2014.
Related Links
If these Tamil asylum seekers have been handed over to the Sri Lankan navy, Abbott and his murderous crew should be at the Hague for crimes against humanity.